- Education
- Forex Technical Analysis
- Technical Indicators
- Trend Indicators
- Standard Deviation Indicator
Standard Deviation Indicator
In the fast-paced and dynamic world of trading, successful traders are constantly seeking tools and techniques to gain an edge in the markets. One such indispensable tool is the Standard Deviation (SD) indicator, a statistical measure that provides valuable insights into market volatility and risk. By harnessing the power of the Standard Deviation Indicator, traders can make more informed decisions and navigate the complexities of financial markets with confidence.
In this article we are going to learn Standard Deviation Indicator in the field of trading. Whether you're a novice trader exploring technical analysis or an experienced professional looking to refine your strategies, this article will equip you with the knowledge to leverage the Standard Deviation Indicator effectively.

Key points to be covered in the article:
- What is standard deviation
- How to use the standard deviation
- Standard deviation formula
- How to calculate standard deviation
- How to interpret standard deviation
By understanding Standard Deviation Indicator, traders can gain valuable insights into market volatility, make more informed decisions, and refine their trading strategies. Whether you're seeking to identify optimal entry and exit points or manage risk effectively, the Standard Deviation Indicator can play a big role in your trading journey.
What is Standard Deviation
Standard deviation is a statistical measure that helps us understand how spread out or varied a set of numbers is. It tells us how much the individual numbers in a group differ from the average (or mean) of that group.
Imagine you have a group of numbers, like 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10. The average of these numbers is 6. The standard deviation would give us an idea of how far each number deviates from this average.
If the numbers in the group are close to the average, the standard deviation will be small. But if the numbers are more spread out, the standard deviation will be larger.
For example, let's consider another group of numbers: 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. The average is still 6, but the numbers are closer to the average compared to the first group. Therefore, the standard deviation for this group would be smaller.
In essence, the standard deviation helps us understand the "typical" distance between each data point and the average. It provides a measure of how much the numbers in a group vary from the average, giving us insights into the overall variability or dispersion of the data set.
By calculating and interpreting the standard deviation, we can gain a better understanding of the patterns and characteristics of a set of numbers, making it a valuable tool in various fields such as finance, statistics, and data analysis.
How to Use the Standard Deviation
The standard deviation indicator can be a valuable tool for assessing market volatility and making trading decisions. Here's how you can use it:
- Identifying Volatility
- Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
- Assessing Risk and Reward
- Detecting Market Conditions
- Combining with Other Indicators
1. Identifying Volatility
The standard deviation indicator helps you understand the level of volatility in the forex market. When the standard deviation is high, it suggests that the currency pair's prices have been experiencing significant fluctuations. This can indicate a more volatile market, which may present both opportunities and risks for traders.
2. Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
By analyzing the standard deviation, you can determine appropriate stop loss and take profit levels for your trades. A higher standard deviation implies wider price swings, and you might consider setting wider stop loss levels to accommodate potential market noise. Conversely, a lower standard deviation might allow for tighter stop loss levels.
3. Assessing Risk and Reward
The standard deviation can assist in evaluating the risk and reward potential of forex trades. When the standard deviation is higher, it suggests a higher degree of risk. Traders might adjust their position sizes or risk management strategies accordingly. Similarly, a lower standard deviation might indicate a lower level of risk.
Fore example:
Price: 1.2000 1.2100 1.2200 1.2300 1.2400 1.2500
Standard deviation = 0.01
Risk = 1 standard deviation = 0.01
Reward = 2 standard deviations = 0.02
Risk/Reward = 1/2 = 1:2
In this example, the standard deviation is 0.01, which means that the price is likely to fluctuate within a range of 0.01 around the mean price of 1.2200. The risk of a trade is therefore equal to one standard deviation, or 0.01. The reward of a trade is two standard deviations, or 0.02. The risk/reward ratio for this trade is therefore 1:2, which means that for every 1 unit of risk, the trader stands to make 2 units of reward.
Of course, this is just a simple example. The actual risk and reward of a trade will depend on a number of factors, including the volatility of the market, the size of the position, and the stop-loss and profit target levels. However, the standard deviation can be a useful tool for assessing the risk and reward potential of forex trades.
4. Detecting Market Conditions
Changes in the standard deviation can help identify shifts in market conditions. For example, a sudden increase in the standard deviation might signify increased market uncertainty, such as during economic news releases or geopolitical events. Traders can use this information to adapt their trading strategies or consider waiting for the market to stabilize before entering trades.
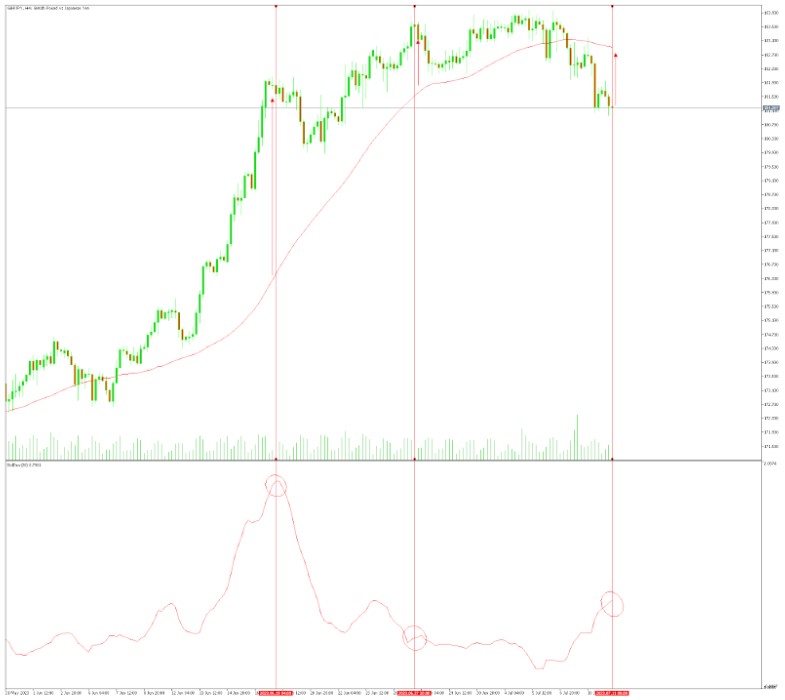
5. Combining with Other Indicators
To enhance your trading analysis, you can combine the standard deviation indicator with other technical indicators. For instance, using the standard deviation alongside trend-following indicators like moving averages can provide a comprehensive view of the market, helping you identify potential entry and exit points.
Remember that the standard deviation indicator is just one tool in your trading toolkit, and it should be used in conjunction with other analysis methods and indicators. Forex trading involves inherent risks, and no single indicator can guarantee success. It's important to practice proper risk management, conduct thorough analysis, and consider multiple factors when making trading decisions.
Standard Deviation Formula
The formula for calculating the standard deviation is as follows:
Standard Deviation = √(Σ((x - μ)^2) / N)
Where:
x represents each data point in the data set.
μ denotes the mean (average) of the data set.
Σ signifies the summation (addition) of all values.
N represents the total number of data points in the data set.
How to Calculate Standard Deviation
To break it down step-by-step:
- Calculate the mean (average) of the data set by summing up all the data points and dividing by the total number of data points:
μ = (x1 + x2 + x3 + ... + xn) / N - Subtract the mean from each data point:
(x - μ) - Square the result of each subtraction:
(x - μ)^2 - Calculate the sum of all the squared differences:
Σ((x - μ)^2) - Divide the sum obtained in step 4 by the total number of data points (N):
Σ((x - μ)^2) / N - Finally, take the square root of the result obtained in step 5 to get the standard deviation:
Standard Deviation = √(Σ((x - μ)^2) / N)
Formula looks complicated for an untrained eye, but the essence of it is quite simple;
In practical terms, standard deviation helps us analyze and interpret data. It allows us to compare different sets of numbers, assess risks in finance and investing, identify unusual observations, and make more informed decisions based on the level of variation present in the data.
Ultimately, the essence of standard deviation is to provide a numerical value that represents how much the data points deviate from the average, helping us understand the overall spread or variability of the data set.
How to Interpret Standard Deviation
Here are some ways to interpret standard deviation on forex currency pairs:
| Standard Deviation | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| High | - Indicates a volatile currency pair - Potential for wide price fluctuations - Attractive for traders seeking high-profit opportunities - Higher risk due to increased volatility |
| Low | - Indicates a less volatile currency pair - Price tends to move within a narrower range - Attractive for traders looking for stability and lower risk - Lower profit potential compared to highly volatile pairs |
| Comparison toprevious periods | - Useful for assessing changes in volatility over time - Higher standard deviation suggests increasing volatility - Lower standard deviation indicates decreasing volatility |
| Comparison to other currency pairs | - Helps identify the most and least volatile currency pairs - Traders can select currency pairs based on their risk appetite and trading goals - Provides a relative measure of volatility among different currency pairs |
EUR/USD example of how to interpret standard deviation on a currency pair:
Let's say the standard deviation of the EUR/USD currency pair is 0.01. This means that the EURUSD price is likely to fluctuate within a range of 0.01 around the mean price. So, if the mean price of the EUR/USD is 1.2000, then the price could be anywhere between 1.1990 and 1.2010.
If the standard deviation is higher, for example 0.02, then the price of the EUR/USD is likely to fluctuate within a range of 0.02 around the mean price. So, if the mean price of the EUR/USD is 1.2000, then the price could be anywhere between 1.1800 and 1.2200.
A higher standard deviation indicates that the currency pair is more volatile. This means that the price is likely to fluctuate more widely over a period of time. Traders who are looking to trade in volatile markets may find this currency pair attractive, as there is the potential to make large profits. However, it is important to remember that there is also a higher risk of losing money in volatile markets.
A lower standard deviation indicates that the currency pair is less volatile. This means that the price is likely to move within a narrower range over a period of time. Traders who are looking to trade in less volatile markets may find this currency pair attractive, as there is less risk of losing money. However, it is important to remember that there is also less potential to make large profits in less volatile markets.
Bottom line on Standard Deviation Indicator
In conclusion, the standard deviation indicator is a statistical measure of volatility. It is used to measure how much prices fluctuate around their average value. A high standard deviation indicates that prices are volatile and tend to move up and down a lot, while a low standard deviation indicates that prices are more stable and tend to move within a narrower range.
The standard deviation indicator can be used to identify periods of high and low volatility. This information can be helpful for traders who want to trade in volatile markets or who want to avoid trading in volatile markets. The standard deviation indicator can also be used to set stop-losses and profit targets.
However, it is important to remember that the standard deviation indicator is just one tool, and it should not be used in isolation. Other factors should also be considered when making trading decisions.
Forex Indicators FAQ
What is a Forex Indicator?
Forex technical analysis indicators are regularly used by traders to predict price movements in the Foreign Exchange market and thus increase the likelihood of making money in the Forex market. Forex indicators actually take into account the price and volume of a particular trading instrument for further market forecasting.
What are the Best Technical Indicators?
Technical analysis, which is often included in various trading strategies, cannot be considered separately from technical indicators. Some indicators are rarely used, while others are almost irreplaceable for many traders. We highlighted 5 the most popular technical analysis indicators: Moving average (MA), Exponential moving average (EMA), Stochastic oscillator, Bollinger bands, Moving average convergence divergence (MACD).
How to Use Technical Indicators?
Trading strategies usually require multiple technical analysis indicators to increase forecast accuracy. Lagging technical indicators show past trends, while leading indicators predict upcoming moves. When selecting trading indicators, also consider different types of charting tools, such as volume, momentum, volatility and trend indicators.
Do Indicators Work in Forex?
There are 2 types of indicators: lagging and leading. Lagging indicators base on past movements and market reversals, and are more effective when markets are trending strongly. Leading indicators try to predict the price moves and reversals in the future, they are used commonly in range trading, and since they produce many false signals, they are not suitable for trend trading.

